Vignette: Sex-chromosome bias-corrected reference signals from pooled average
Author: Henrik Bengtsson
Created on: 2009-09-19
Updated on: 2015-04-17
This document illustrates how to (i) use a sample annotation file to specify the gender of samples, and how to (ii) calculate a pooled copy-number reference that is corrected for sample biases due to difference in sex chromosomes. This gender-aware bias correction is described in Section '3.2.7 Reference signals' of Bengtsson, Irizarry, Carvalho, and Speed (2008).
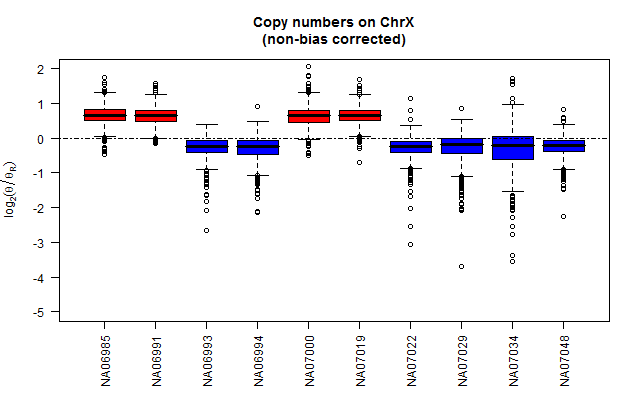
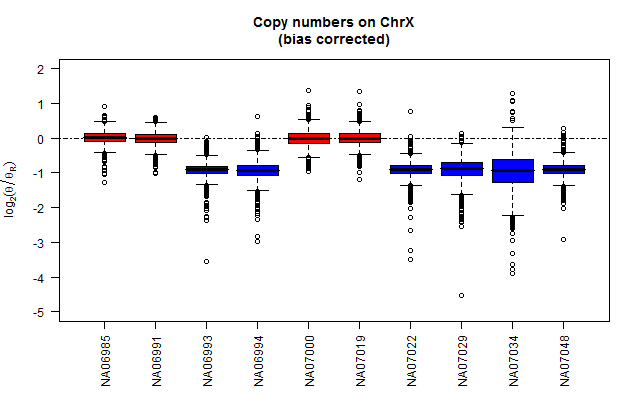
In the below figure, the top and bottom panels show chromosome X copy-number estimates with and without bias correction.
Setup
Here we will use 10 public Mapping50K_Hind240 CEL files from the HapMap project.
Raw data
Download the following CEL files from the HapMap site (see the 'HapMap 100K' data set on Page Data Sets):
rawData/
HapMap,CEU,testSet/
Mapping50K_Hind240/
NA06985_Hind_B5_3005533.CEL
NA06991_Hind_B6_3005533.CEL
NA06993_Hind_B4_4000092.CEL
NA06994_Hind_A7_3005533.CEL
NA07000_Hind_A8_3005533.CEL
NA07019_Hind_A12_4000092.CEL
NA07022_Hind_A10_4000092.CEL
NA07029_Hind_A9_4000092.CEL
NA07034_Hind_B1_4000092.CEL
NA07048_Hind_B3_4000092.CEL
Sample annotation data
Download the HapMap270.saf sample annotation file (SAF) and place it in:
annotationData/
samples/
HapMap270.saf
For more details on what SAF files are and how to setup new ones, see section below.
Chip-type annotation data
Download the following annotation files (Mapping50K_Hind240 & Mapping50K_Xba240):
annotationData/
chipTypes/
Mapping50K_Hind240/
Mapping50K_Hind240.CDF
Mapping50K_Hind240,na26,HB20080916.ufl
Mapping50K_Hind240,na26,HB20080916.ugp
Startup
library("aroma.affymetrix")
library("R.devices")
devOptions("png", width=1024)
# Use a nicer palette of colors
colors <- RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(12, "Paired")
palette(colors)
# Setup the Verbose object
verbose <- Arguments$getVerbose(-10, timestamp=TRUE)
Setup of chip-type annotation data
cdf <- AffymetrixCdfFile$byChipType("Mapping50K_Hind240")
print(cdf)
# Assert existence of Aroma UFL, UGP and ACS files needed
# by the CRMA/CRMA v2 preprocessing methods
# (these test are optional but it's helpful to check here)
acs <- getAromaCellSequenceFile(cdf)
ugp <- getAromaUgpFile(cdf)
ufl <- getAromaUflFile(cdf)
Setup of sample annotation files (SAFs)
DISCLAIMER: The use of SAFs should be considered be in an alpha stage, that is, the format and the usage might change over time and backward compatibility is not guaranteed.
The SAF file format is a text-based file format that is specific to aroma.affymetrix. A SAF file contains one or more records, where each record specify additional attributes for a unique sample, e.g. the gender or equivalently the ploidy of ChrX and ChrY. Here is what the SAF record for HapMap sample NA06991 looks like:
name: NA06991
familyID: 1341
individualID: 2
fatherID: 13
motherID: 14
gender: female
population: CEU
tags: XX
The name attribute is used to map the record to the name (the fullname without the comma-separated tags) of an existing array (or vice versa).
When loading a CEL set (including chip-effect sets), the annotationData/samples/ directory is scanned for *.saf files and all SAF records are loaded and matched against the names of the arrays loaded). When a match is found, the attributes specified by the SAF record is automatically added to the array object. As we will see below, attributes for a sample/array can be retrieved as:
cf <- csR[[indexOf(csR, "NA06991")]]
attrs <- getAttributes(cf)
str(attrs)
List of 9
$ familyID : chr "1341"
$ fatherID : chr "13"
$ force : logi FALSE
$ gender : chr "female"
$ individualID: chr "2"
$ motherID : chr "14"
$ n23 : int 2
$ n24 : int 0
$ population : chr "CEU"
Special attributes 'n23' and 'n24' specifies the ploidy of ChrX (23) and ChrY (24). These attributes are in this case inferred from the 'tags' attribute (not 'gender'), which specifies 'XX'. If 'XY' was given, the attributes would be parsed to be n23=1 and n24=1. An 'XXXY' tag would give n23=3, and n24=1 and so on.
Important: It is never the 'gender' attribute that is used to infer the ploidy on ChrX and ChrY. The reason for this is that genders "male" and "female" does not uniquely specify the number of X and Y chromosomes, e.g. a female may have XXX or XXY and so on. This is a good reason for not talking about "gender" when referring to sex-chromosome ploidy.
Brief about the 'tags' attribute
It is possible to specify the 'n23' and 'n24' attributes of a sample without using a SAF file. For instance, by renaming a file 'NA06991.CEL' to 'NA06991,XX.CEL', the tag 'XX' will recognized to specify the ChrX and ChrY ploidy and attributes 'n23' and 'n24' will be set accordingly.
However, in order to not have to rename the data files, the 'tags' attribute of a SAF record can be used to add tags that are not specified by the filename itself and override (but never remove) existing ones. In other words, if the filename would be 'NA06991,XXXY.CEL', the 'tags' attribute (='XX') in the SAF record would override the 'XXXY' of the filename, and the inferred ploidy would be n23=2 and n24=0.
To be more explicit, one may specify the 'tags' attribute as 'tags: n23=2, n24=0' instead of 'tags: XX'. This format also allows us to specify the ploidy of other chromosomes. For instance:
tags: XY, n21=3
will set the Chr21 ploidy to 3 (trisomy 21) in addition to the ploidy on the sex chromosomes.
Creating custom SAFs
SAF records for multiple samples can be place in one or many *.saf files. If put in the same file, then each record is considered to start with the 'name:' line and end at the last non-empty line before the next SAF record (the next occurrence of 'name:').
Currently the name of the SAF is not important as long as it has extension *.saf; all SAF files are scanned for matching samples.
Please study the above HapMap SAF file for further details.
DISCLAIMER: The SAF file format should be considered to be in alpha stage (=under development). The format might change and we will not guarantee the code to be backward compatible, i.e. when/if the format changes existing SAF files probably have to be updated manually.
Setup of raw data set
csR <- AffymetrixCelSet$byName("HapMap,CEU,testSet", cdf=cdf)
print(getFullNames(csR))
## [1] "NA06985_Hind_B5_3005533" "NA06991_Hind_B6_3005533"
## [3] "NA06993_Hind_B4_4000092" "NA06994_Hind_A7_3005533"
## [5] "NA07000_Hind_A8_3005533" "NA07019_Hind_A12_4000092"
## [7] "NA07022_Hind_A10_4000092" "NA07029_Hind_A9_4000092"
## [9] "NA07034_Hind_B1_4000092" "NA07048_Hind_B3_4000092"
The CEL files downloaded from HapMap has file names such as NA07000_Hind_A8_3005533.CEL. In order for aroma.affymetrix to identify 'NA07000' as the sample name, and 'A8' and '3005533' as tags (ignore the 'Hind' part), we will utilize so called fullname translators that translates the full name to a comma-separated fullname, e.g. 'NA07000_Hind_A8_3005533' to 'NA07000,A8,3005533'.
setFullNamesTranslator(csR, function(names, ...) {
# Turn into comma-separated tags
names <- gsub("_", ",", names)
# Drop any Hind/Xba tags
names <- gsub(",(Hind|Xba)", "", names)
names
})
print(getFullNames(csR))
## [1] "NA06985,B5,3005533" "NA06991,B6,3005533"
## [3] "NA06993,B4,4000092" "NA06994,A7,3005533"
## [5] "NA07000,A8,3005533" "NA07019,A12,4000092"
## [7] "NA07022,A10,4000092" "NA07029,A9,4000092"
## [9] "NA07034,B1,4000092" "NA07048,B3,4000092"
print(csR)
## AffymetrixCelSet:
## Name: HapMap
## Tags: CEU,testSet
## Path: rawData/HapMap,CEU,testSet/Mapping50K_Hind240
## Platform: Affymetrix
## Chip type: Mapping50K_Hind240
## Number of arrays: 10
## Names: NA06985, NA06991, ..., NA07048
## Time period: 2004-01-14 14:02:08 -- 2004-02-13 11:51:01
## Total file size: 244.78MB
## RAM: 0.01MB
Verifying ploidy of ChrX and ChrY
Given that there exists a SAF file as above and that the fullname translators correctly translates the default fullnames of the CEL files to comma-separated ones, aroma.affymetrix will be able to map sample names specified by the files to SAF records and assign the correct ChrX and ChrY ploidy attributes.
To extract the 'n23' and 'n24' attributes from all samples, do:
nXY <- t(sapply(csR, function(cf) getAttributes(cf)[c("n23", "n24")]))
rownames(nXY) <- getNames(csR)
print(nXY)
which gives:
n23 n24
NA06985 2 0
NA06991 2 0
NA06993 1 1
NA06994 1 1
NA07000 2 0
NA07019 2 0
NA07022 1 1
NA07029 1 1
NA07034 1 1
NA07048 1 1
Preprocessing (CEL files to copy-number signals)
After having made sure everything above is correct, we next preprocess and summarize the raw CEL file data to obtain one copy-number signal per locus. Here we the CRMA (v1) method (Bengtsson, Irizarry, Carvalho, et al., 2008).
res <- doCRMAv1(csR, drop=FALSE)
cesN <- res$cesN # ChipEffectSet
print(cesN)
For modern chip types, such as GenomeWideSNP_6, it's recommended to use doCRMAv2() instead, which processes the data using the CRMA v2 method (Bengtsson, Wirapati, and Speed, 2009).
Before continuing, lets convince ourselves that the 'n23' and 'n24' attributes are also reflected in the chip effects returned:
nXY <- t(sapply(cesN, function(cf) getAttributes(cf)[c("n23", "n24")]))
rownames(nXY) <- getNames(cesN)
print(nXY)
Calculate sex-chromosome bias-corrected reference signals
# For Chr1-22 and ChrX the copy-neutral ploidy should be two.
# If the ploidy of a sample is unknown, assume the default is two.
ceRef <- calculateBaseline(cesN, chromosomes=1:23, ploidy=2,
defaultPloidy=2, verbose=verbose)
# For ChrY the ploidy of the reference should be one. Currently our model
# cannot adjust it to be two, because there must be at least one sample
# with the target ploidy.
# ceRef <- calculateBaseline(cesN, chromosomes=24, ploidy=1, verbose=verbose)
# The calculated baseline/reference file is a chip effect file as any other file
print(ceRef)
Segmentation using the above copy-neutral reference
cbs <- CbsModel(cesN, ceRef)
print(cbs)
# Verify that the ChrX CNs are bias corrected
M <- NULL
for (kk in 1:nbrOfArrays(cbs)) {
rawCNs <- extractRawCopyNumbers(cbs, array=kk, chromosome=23)
rawCNs <- as.data.frame(rawCNs)$cn
M <- cbind(M, rawCNs)
}
colnames(M) <- getArrays(cbs)
n23 <- sapply(cesN, getAttribute, "n23")
col <- c("blue", "red")[n23]
Mlab <- expression(log[2](theta/theta[R]))
Mlim <- c(-5,2)
toPNG("ChrX", tags=c("biasCorrected"), aspectRatio=0.618, {
boxplot(as.data.frame(M), col=col, ylim=Mlim, ylab=Mlab, las=2)
abline(h=0, lty=4)
title("Copy numbers on ChrX\n(bias corrected)")
})
To do the actual segmentation, do:
process(cbs, verbose=verbose)
See other vignettes for further details.
What it looks like without correction
cbs2 <- CbsModel(cesN)
print(cbs2)
# Verify that the ChrX CNs are bias corrected
M2 <- NULL
for (kk in 1:nbrOfArrays(cbs2)) {
rawCNs <- extractRawCopyNumbers(cbs2, array=kk, chromosome=23)
rawCNs <- as.data.frame(rawCNs)$cn
M2 <- cbind(M2, rawCNs)
}
colnames(M2) <- getArrays(cbs2)
toPNG("ChrX", tags=c("nonCorrected"), aspectRatio=0.618, {
boxplot(as.data.frame(M2), col=col, ylim=Mlim, ylab=Mlab, las=2)
abline(h=0, lty=4)
title("Copy numbers on ChrX\n(non-bias corrected)")
})
References
[1] H. Bengtsson, R. Irizarry, B. Carvalho, et al. "Estimation and assessment of raw copy numbers at the single locus level". Eng. In: Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 24.6 (Mar. 2008), pp. 759-67. ISSN: 1367-4811. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn016. PMID: 18204055.
[2] H. Bengtsson, P. Wirapati, and T. P. Speed. "A single-array preprocessing method for estimating full-resolution raw copy numbers from all Affymetrix genotyping arrays including GenomeWideSNP 5 & 6". Eng. In: Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 25.17 (Sep. 2009), pp. 2149-56. ISSN: 1367-4811. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp371. PMID: 19535535.